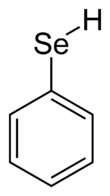
Benzeneselenol
Benzeneselenol, also known as selenophenol, is the organoselenium compound with the formula C6H5SeH, often abbreviated PhSeH. It is the selenium analog of phenol. This colourless, intensely malodorous compound is a useful reagent in organic synthesis.[1]
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
benzeneselenol | |||
| Other names
Selenaphenol, selenophenol, phenylselenol | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.417 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID |
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H6Se | |||
| Molar mass | 157.07 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | colorless liquid | ||
| Odor | extremely foul yet characteristic | ||
| Density | 1.479 g/cm3 | ||
| Boiling point | 71 to 72 °C (160 to 162 °F; 344 to 345 K) (18 mm Hg) | ||
| slightly | |||
| Solubility in other solvents | most organic solvents | ||
Refractive index (nD) |
1.616 | ||
| Structure | |||
| 1.1 D | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards |
toxic | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||
   | |||
| Danger | |||
| H301, H331, H373, H410 | |||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds |
Thiophenol, Hydrogen selenide, Diphenyl diselenide | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |||
Synthesis
Benzeneselenol is prepared by the reaction of phenylmagnesium bromide and selenium:[2]
- PhMgBr + Se → PhSeMgBr
- PhSeMgBr + HCl → PhSeH + MgBrCl
Reactions
More so than thiophenol, benzeneselenol is easily oxidized by air. The facility of this reaction reflects the weakness of the Se-H bond. The product is diphenyl diselenide as shown in this idealized equation:
- 4 PhSeH + O2 → 2 PhSeSePh + 2 H2O
The presence of the diselenide in benzeneselenol is indicated by a yellow coloration. The diselenide can be converted back to the selenol by reduction followed by acidification of the resulting PhSe−.
PhSeH is acidic with a pKa of 5.9. Thus at neutral pH, it is mostly ionized:
- PhSeH → PhSe− + H+
It is approximately seven times more acidic than the related thiophenol. Both compounds dissolve in water upon the addition of base. The conjugate base is PhSe−, a potent nucleophile.[1]
History
Benzeneselenol was first reported in 1888 by the reaction of benzene with selenium tetrachloride (SeCl4) in the presence of aluminium trichloride (AlCl3).[3][4]
Safety
The compound is intensely malodorous[5] and, like other organoselenium compounds, toxic.
References
- Sonoda, Noboru; Ogawa, Akiya; Recupero, Francesco (2005). "Benzeneselenol". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rb018.pub2. ISBN 0471936235.
- Foster, D. G. (1944). "Selenophenol". Organic Syntheses. 24: 89. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.024.0089.
- Chabrié, M. C. (1888). "Premiers essais de synthèse de composés organiques séléniés dans la série aromatique". Bulletin de la Société Chimique de Paris. 50: 133–137.
- Chabrié, M. C. (1890). "Sur la synthèse de quelques composés séléniés dans la série aromatique". Annales de Chimie et de Physique. 6 (20): 202–286.
- Lowe, D. (2012-05-15). "Things I wont work with: Selenophenol". In the Pipeline.