Norpsilocin
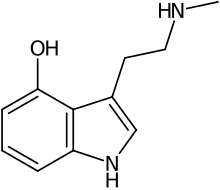
Norpsilocin or 4-HO-NMT is naturally occurring tryptamine alkaloid recently discovered in 2017 in one species called Psilocybe cubensis.[1][2] It is said to be dephosphorylated metabolite of baeocystin however this hypothesis haven't been formally proven.[2] Norpsilocin was found to be a full agonist of 5-HT2A receptor. It is also more potent than psilocin.[3][4]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-[2-(methylamino)ethyl]-1H-indol-4-ol | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H14N2 | |
| Molar mass | 174.247 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
See also
References
- Lenz C, Wick J, Hoffmeister D (October 2017). "Identification of ω-N-Methyl-4-hydroxytryptamine (Norpsilocin) as a Psilocybe Natural Product". Journal of Natural Products. 80 (10): 2835–2838. doi:10.1021/acs.jnatprod.7b00407. PMID 28929753.
- "Two New Crystalline Forms of Norpsilocin".
- "Study Finds Norpsilocin is More Potent Than Psilocin at 5-HT2A".
- Sherwood AM, Halberstadt AL, Klein AK, McCorvy JD, Kaylo KW, Kargbo RB, Meisenheimer P (February 2020). "Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Tryptamines Found in Hallucinogenic Mushrooms: Norbaeocystin, Baeocystin, Norpsilocin, and Aeruginascin". Journal of Natural Products. 83 (2): 461–467. doi:10.1021/acs.jnatprod.9b01061. PMID 32077284.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.