List of railway lines in Bulgaria
This is a list of railway lines in Bulgaria focusing primarily on intercity train lines. In 2019, there were 4,071 kilometres (2,530 mi) of standard gauge railways, of which 67% were electrified.[1] Narrow gauge lines amount to 125 kilometres (78 mi).[2]
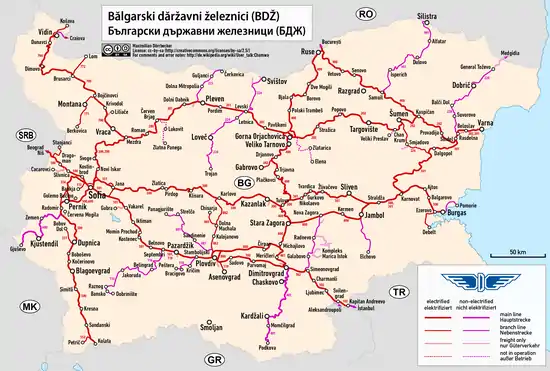
Train railways, as well as related infrastructure such as stations, are managed and maintained by the National Railway Infrastructure Company, which split from Bulgarian State Railways (BDZ) - Bulgaria's national rail company - in 2002. The State Enterprice National Company Railway Infrastructure (rail-infra.bg web site) holds a virtual monopoly on ownership and works closely with the State Railways.
Non-train rail transport in Bulgaria is limited to tram and metro services in Sofia, both managed by their own municipality-owned companies.
Active lines
Bolded indicates main lines. Italics indicate narrow-gauge lines.
| Name | Route | Length | Gauge | Electrified | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BDZ Line 1 | Kalotina – Sofia – Plovdiv – Svilengrad | 356 km (221 mi) | Standard | Yes | Freight & passenger |
| BDZ Line 2 | Sofia – Mezdra – Gorna Oryahovitsa – Kaspichan – Varna | 544 km (338 mi) | Standard | Yes | Freight & passenger |
| BDZ Line 3 | Iliyantsi – Tulovo – Dabovo – Zimnitsa – Karnobat – Sindel – Varna (ferry) | 541 km (336 mi) | Standard | Yes | Freight & passenger |
| BDZ Line 4 | Ruse – Gorna Oryahovitsa – Dabovo – Tulovo – Stara Zagora – Mihaylovo – Podkova | 415 km (258 mi) | Standard | Yes | Freight & passenger |
| BDZ Line 5 | Sofia – Pernik – Radomir – Kulata | 209 km (130 mi) | Standard | Yes | Freight & passenger |
| BDZ Line 6 | Voluyak – Pernik – Gyueshevo | 134 km (83 mi) | Standard | Yes | Freight & passenger |
| BDZ Line 7 | Mezdra – Boychinovtsi – Brusartsi – Vidin | 181 km (112 mi) | Standard | Yes | Freight & passenger |
| BDZ Line 8 | Plovdiv – Stara Zagora – Yambol – Karnobat – Burgas | 293 km (182 mi) | Standard | Yes | Freight & passenger |
| BDZ Line 9 | Ruse – Samuil – Kaspichan | 137 km (85 mi) | Standard | Yes | Freight & passenger |
| BDZ Line 11 | Kalotina – Stanyantsi | 16 km (10 mi) | Standard | No | Freight only |
| BDZ Line 13 | Sofia – Voluyak – Bankya | 11 km (7 mi) | Standard | No | Passenger only |
| [[Septemvri–Dobrinishte narrow-gauge [760 mm 29,92 inches] line|BDZ Line 16]] | Septemvri – Dobrinishte | 125 km (78 mi) | Narrow | No | Passenger only |
| BDZ Line 18 | Stamboliyski – Peshtera | 28 km (17 mi) | Standard | No | Passenger only |
| BDZ Line 19 | Krumovo – Asenovgrad | 10 km (6 mi) | Standard | Yes | Passenger only |
| BDZ Line 23 | Yasen – Cherkovitsa | 43 km (27 mi) | Standard | No | Passenger only |
| BDZ Line 24 | Svishtov – Levski – Troyan | 130 km (81 mi) | Standard | No | Passenger only |
| BDZ Line 27 | Shumen – Komunari | 50 km (31 mi) | Standard | Yes | Passenger only |
| BDZ Line 28 | Povelyanovo – Kardam | 109 km (68 mi) | Standard | Partially | Freight & passenger |
| BDZ Line 42 | Tsareva Livada – Gabrovo | 17 km (11 mi) | Standard | Yes | Passenger only |
| BDZ Line 51 | Dupnitsa – Bobov Dol | 19 km (12 mi) | Standard | Yes | Freight only |
| BDZ Line 52 | General Todorov – Petrich | 9 km (6 mi) | Standard | Yes | Passenger only |
| BDZ Line 71 | Boychinovtsi – Berkovitsa | 38 km (24 mi) | Standard | Yes | Passenger only |
| BDZ Line 72 | Brusartsi – Lom | 23 km (14 mi) | Standard | Yes | Passenger only |
| BDZ Line 73 | Vidin – Koshava | 28 km (17 mi) | Standard | Partially | Freight only |
| BDZ Line 81 | Filipovo – Panagyurishte | 71 km (44 mi) | Standard | No | Freight & passenger |
| BDZ Line 82 | Filipovo – Dolna Mahala – Karlovo | 65 km (40 mi) | Standard | Yes | Freight & passenger |
| BDZ Line 82.1 | Dolna Mahala – Hisarya | 15 km (9 mi) | Standard | Yes | Passenger only |
| BDZ Line 83 | Simeonovgrad – Nova Zagora | 111 km (69 mi) | Standard | Ongoing | Freight & passenger |
| BDZ Line 91 | Samuil – Silistra | 113 km (70 mi) | Standard | No | Passenger only |
Urban rail transport
The capital Sofia is the only Bulgarian city with an urban rail network. These include trams and subway trains. Until 1964, a ring railway connected a number of train stations within Sofia. This abandoned railway has seen renewed interest in 2019, with proposals to either partially restore and use it for connections to Sofia Airport and subway stations, convert it into a "green ring route" for bicycles, or both.[3] In May 2020, it was decided that parts of this railway will not be restored for train movement, but for bicycles and pedestrians instead.[4]
Sofia's urban rail network is nevertheless integrated with the national railway network. Both the tram network and Sofia Metro have stations at Sofia Central Station, the central hub for several of the main train lines in Bulgaria.
Trams
Operational since 1901, the tram network had 137 kilometres (85 mi) of track in 2016, servicing 14 lines with a total two-way route length of 286 kilometres (178 mi). The Sofiya tram network uses two gauges - 1009 mm (39,72 inches) and standard 1435 mm (56,49 inches).[5]
Metro
The only subway system in operation is also located in Sofia. It was unveiled in 1998 and has four lines with a total length of 52 km 32 mi and 47 stations.[6] metropolitan.bg web site
See also
References
- "Map of the railway network in the Republic of Bulgaria". Bulgarian State Railways. Bulgarian State Railways. Retrieved 15 December 2019.
- "Field listing: Railways". CIA The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 15 December 2019.
- "Green ring, ring railroad, or both?". Kapital. Retrieved 12 July 2020.
- "Green ring in Sofia starting next year". 24 Chasa. Retrieved 12 July 2020.
- "Report on Transport" (PDF). Vision for Sofia. 2: 76–81. 2016.
- "About - Metro Sofia". Retrieved 12 July 2020.