BAT5
Protein BAT5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BAT5 gene.[5][6][7]
| ABHD16A | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | ABHD16A, BAT5, D6S82E, NG26, PP199, abhydrolase domain containing 16A, hBAT5, abhydrolase domain containing 16A, phospholipase, SPG86 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 142620 MGI: 99476 HomoloGene: 10904 GeneCards: ABHD16A | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Orthologs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Species | Human | Mouse | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Entrez | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ensembl |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 6: 31.69 – 31.7 Mb | Chr 17: 35.31 – 35.32 Mb | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
A cluster of genes, BAT1-BAT5, has been localized in the vicinity of the genes for TNF alpha and TNF beta. These genes are all within the human major histocompatibility complex class III region. The protein encoded by this gene is thought to be involved in some aspects of immunity.[7]
Bat5 structure
Amino Acid Sequence

BAT5 (also known as ABHD16A) has been found to be 558 amino acid residues. It was fist identified in 1992 in the gene domain of TNF alpha and TNF beta. BAT5 (ABHD 16A) in different species has been found to be different lengths of amino acid sequence.
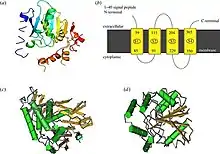
BAT5 has been determined to be highly conserved when compared to human, mice and other mammalian ontologies.[8] It is found to be expressed in multiple different tissue cells. According to molecular evolutionary genetic analysis, in comparison of 13 mammalian species, the noticeable differences in amino acid sequence length is due to splicing in post transcriptional processing of mRNA.[9]
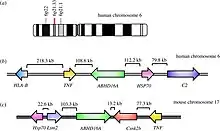
BAT5 gene location
Human Bat5 (ABHD16A) is located on chromosome 6. Mice Bat5 (ABHD 16A) is located between TNF and Heat shock protein near the Ck2b protein kinase gene.[9]
BAT5 molecular weight
_compared_to_mice_(m).png.webp)
BAT5 in humans and mice has been found to be around 63kDA.
Bat5 implications in recent studies
BAT5 has been linked to neurological, immune regulation, Kawasaki's disease and coronary artery disease.[9]
References
- ENSG00000231488, ENSG00000204427, ENSG00000235676, ENSG00000230475, ENSG00000206403, ENSG00000224552 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000236063, ENSG00000231488, ENSG00000204427, ENSG00000235676, ENSG00000230475, ENSG00000206403, ENSG00000224552 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000007036 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Spies T, Blanck G, Bresnahan M, Sands J, Strominger JL (Feb 1989). "A new cluster of genes within the human major histocompatibility complex". Science. 243 (4888): 214–7. Bibcode:1989Sci...243..214S. doi:10.1126/science.2911734. PMID 2911734.
- Spies T, Bresnahan M, Strominger JL (Dec 1989). "Human major histocompatibility complex contains a minimum of 19 genes between the complement cluster and HLA-B". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 86 (22): 8955–8. Bibcode:1989PNAS...86.8955S. doi:10.1073/pnas.86.22.8955. PMC 298409. PMID 2813433.
- "Entrez Gene: BAT5 HLA-B associated transcript 5".
- Savinainen, Juha R.; Patel, Jayendra Z.; Parkkari, Teija; Navia-Paldanius, Dina; Marjamaa, Joona J. T.; Laitinen, Tuomo; Nevalainen, Tapio; Laitinen, Jarmo T. (2014-10-07). "Biochemical and Pharmacological Characterization of the Human Lymphocyte Antigen B-Associated Transcript 5 (BAT5/ABHD16A)". PLOS ONE. 9 (10): e109869. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0109869. ISSN 1932-6203.
- Xu, Jun; Gu, Weizhen; Ji, Kai; Xu, Zhao; Zhu, Haihua; Zheng, Wenming. "Sequence analysis and structure prediction of ABHD16A and the roles of the ABHD family members in human disease". Open Biology. 8 (5): 180017. doi:10.1098/rsob.180017. PMC 5990648. PMID 29794032.
External links
- Human ABHD16A genome location and ABHD16A gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
Further reading
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Gevaert K, Goethals M, Martens L, et al. (2004). "Exploring proteomes and analyzing protein processing by mass spectrometric identification of sorted N-terminal peptides". Nat. Biotechnol. 21 (5): 566–9. doi:10.1038/nbt810. PMID 12665801. S2CID 23783563.
- Mungall AJ, Palmer SA, Sims SK, et al. (2003). "The DNA sequence and analysis of human chromosome 6". Nature. 425 (6960): 805–11. Bibcode:2003Natur.425..805M. doi:10.1038/nature02055. PMID 14574404.
- Xie T, Rowen L, Aguado B, et al. (2004). "Analysis of the Gene-Dense Major Histocompatibility Complex Class III Region and Its Comparison to Mouse". Genome Res. 13 (12): 2621–36. doi:10.1101/gr.1736803. PMC 403804. PMID 14656967.
- Lehner B, Semple JI, Brown SE, et al. (2004). "Analysis of a high-throughput yeast two-hybrid system and its use to predict the function of intracellular proteins encoded within the human MHC class III region". Genomics. 83 (1): 153–67. doi:10.1016/S0888-7543(03)00235-0. PMID 14667819.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Lehner B, Sanderson CM (2004). "A Protein Interaction Framework for Human mRNA Degradation". Genome Res. 14 (7): 1315–23. doi:10.1101/gr.2122004. PMC 442147. PMID 15231747.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Wan D, Gong Y, Qin W, et al. (2004). "Large-scale cDNA transfection screening for genes related to cancer development and progression". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101 (44): 15724–9. Bibcode:2004PNAS..10115724W. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404089101. PMC 524842. PMID 15498874.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. Bibcode:2005Natur.437.1173R. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514. S2CID 4427026.