Anak Krakatoa
Anak Krakatoa (Indonesian: Anak Krakatau) (English: Child of Krakatoa) is an island in a caldera in the Sunda Strait between the islands of Java and Sumatra in the Indonesian province of Lampung.[1] On December 29, 1927, Anak Krakatoa emerged from the caldera formed in 1883 by the explosive volcanic eruption that destroyed the island of Krakatoa.[2]
| Anak Krakatoa | |
|---|---|
_(cropped).jpg.webp) Anak Krakatoa in 2019 | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 288 m (945 ft) |
| Prominence | 110 m (360 ft) |
| Listing | Spesial Ribu |
| Coordinates | 6°06′07″S 105°25′23″E |
| Naming | |
| Native name | Anak Krakatau (Indonesian) |
| Geography | |
 Anak Krakatoa Location | |
| Location | Indonesia |
| Geology | |
| Age of rock | Holocene – very recent |
| Mountain type | Somma-stratovolcano |
| Last eruption | 24 April 2022 |
| Climbing | |
| First ascent | 29 December 1927 |
There has been sporadic eruptive activity at the site since the late 20th century,[3] culminating with a large underwater collapse of the volcano which caused a deadly tsunami in December 2018, followed by subsequent activity in 2019 and an eruption in April 2020. Due to its young age, the island is one of several in the area which are of considerable interest to volcanologists, and the subject of extensive study.
Volcanic activity

Until its 2018 collapse, Anak Krakatau had grown at 13 cm (5.1 in) per week on average since the 1950s. This equates to an average growth of 6.8 m (22 ft) per year. Its most recent eruptive episode began in 1994. Quiet periods of a few days have alternated with almost continuous Strombolian eruptions since then. Hot gases, rocks, and lava were released in an eruption in April 2008. Scientists monitoring the volcano warned people to stay out of a 3 km (1.9 mi) zone around the island.[4]
On 6 May 2009, the Volcanological Survey of Indonesia raised the eruption alert status of Anak Krakatoa to Level 3.[5] An expedition to the volcano revealed that a 100 m (330 ft) wide lava dome was growing in its crater. In January 2012, volcanologists at the University of Oregon warned that a tsunami caused by flank collapse of Anak Krakatoa was likely, as it had formed on a steep slope at an edge of the big caldera formed in 1883.[6]
A new eruptive phase was observed from June 2018, and on 15 October 2018, Anak Krakatau had a strong Strombolian to weak Vulcanian eruption that sent lava bombs into the water.[7][8]
2018 eruption and aftermath
An eruption of the volcano on 22 December 2018 caused a deadly tsunami, with waves up to five meters in height making landfall.[9][10] On 31 December 2018, the disaster agency gave the tsunami's death toll as 437, with 14,059 injured.[11] The tsunami affected more than 186 miles of coastline in Sumatra and Java. More than 420 people died, and 40,000 were displaced.[12] This made the eruption the second deadliest volcanic eruption of the 21st century so far. Cone collapse—with tsunami generation—was considered a potential hazard immediately before the eruption.[10] Scientists had modeled the possibility six years before the event, and had identified the western flank as the section of the volcano most likely to fail.[10]
Following the December 2018 eruption, it was believed that the southwest sector of the volcano, including the summit, had collapsed during the eruption, triggering the tsunami. On 23 December, this was confirmed by satellite data and helicopter footage, with the main conduit seen erupting from underwater, producing Surtseyan-style activity.[13] The volcano lost over two-thirds of its volume due to this event,[14] and its elevation above sea level was reduced from 338 m (1,109 ft) to just 110 m (360 ft).[15][10]
Satellite radar observations showed that by 10 January 2019, the volcano had continued to form, with further eruptions beginning to re-model the remnant structure. The crater, which had become open to the sea immediately after the eruption, now had a complete circle of rim above sea level.[16]
In May 2019, phreatomagmatic activity was observed around the newly-reconstructed crater as the volcano continued to increase in height and remodel the areas destroyed in 2018.[17]
2020 eruption
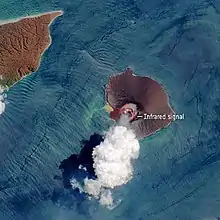
Anak Krakatoa began erupting again on the morning of 10 April 2020. The first eruption could be heard in the Indonesian capital of Jakarta, over 150 kilometres (93 mi) away spewing out a 200 metres (660 ft) high column of ash and smoke according to the Center for Volcanology and Geological Disaster Mitigation’s (PVMBG) magma volcanic activity report, which also said that the first eruption lasted one minute and 12 seconds starting at 9:58 p.m.[18] The eruption spewed ash to about 14 kilometres (46,000 ft) and a secondary ash plume made it to about 11 kilometres (36,000 ft). The eruption was largely magmatic with lava fountains visible. No widespread damage was reported, and the eruption ended several hours later.[19]
2022 eruption
According to the Indonesian Geological Agency, Anak Krakatoa erupted on 4 February 2022 and 5 February 2022.[20]
On 24 April, at 8:20 PM, Anak Krakatoa erupted, sending a massive plume of ash 3,157 metres above the sea level. The mountain has erupted 21 times in recent weeks, but 24 April eruption is the biggest eruption on April.[21] On 26 April, Meteorology, Climatology, and Geophysical Agency (BMKG) increased the alert level for Anak Krakatoa from level 2 to level 3, signifying the need for standby.[22] The agency also warned of possible high waves and tsunami that night.[23][24]
See also
References
- "Krakatoa". Global Volcanism Program. Smithsonian Institution. Retrieved 6 January 2021.
- Gardner, Màiri F.; Troll, Valentin R.; Gamble, John A.; Gertisser, Ralf; Hart, Garret L.; Ellam, Rob M.; Harris, Chris; Wolff, John A. (1 January 2013). "Crustal Differentiation Processes at Krakatau Volcano, Indonesia". Journal of Petrology. 54 (1): 149–182. doi:10.1093/petrology/egs066. ISSN 0022-3530. Archived from the original on 5 January 2022. Retrieved 30 September 2020.
- Dahren, Börje; Troll, Valentin R.; Andersson, Ulf B.; Chadwick, Jane P.; Gardner, Màiri F.; Jaxybulatov, Kairly; Koulakov, Ivan (1 April 2012). "Magma plumbing beneath Anak Krakatau volcano, Indonesia: evidence for multiple magma storage regions". Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology. 163 (4): 631–651. doi:10.1007/s00410-011-0690-8. ISSN 1432-0967. S2CID 52064179. Archived from the original on 18 January 2022. Retrieved 4 February 2021.
- Supriyatin (11 November 2007). "Indonesia's Krakatau roars, dazzles with fireworks". Reuters India. Archived from the original on 10 January 2009. Retrieved 10 January 2019.
- "Status G. Anak Krakatau dinaikkan menjadi Siaga (Level III)" [Anak Krakatau's status raised to Alert (Level III)] (in Indonesian). Volcanological Survey of Indonesia. Archived from the original on 6 May 2009. Retrieved 20 March 2012.
- Giachetti, T.; Paris, R.; Kelfoun, K.; Ontowirjo, B. (January 2012). Terry, J. P.; Goff, J. (eds.). "Tsunami Hazard Related to a Flank Collapse of Anak Krakatau Volcano, Sunda Strait, Indonesia". Natural Hazards in the Asia–Pacific Region: Recent Advances and Emerging Concepts. Special Publications. London: Geological Society. 361: 79–90. doi:10.1144/SP361.7. ISSN 0305-8719. S2CID 131173974. Archived from the original on 25 July 2019. Retrieved 15 January 2019.
- "Krakatau volcano (Indonesia): vulcanian explosions - field report 13-19 Oct 2018". www.volcanodiscovery.com. Volcano Discovery. 20 October 2018. Archived from the original on 18 July 2020. Retrieved 4 May 2022.
- Sennert, Sally Kuhn. "Global Volcanism Program | Report on Krakatau (Indonesia) — 20 June-26 June 2018". volcano.si.edu. Archived from the original on 19 May 2021. Retrieved 4 May 2022.
- "Indonesia 'Volcano Tsunami': At least 168 Dead and 745 Injured after [Anuk] Krakatoa Erupts". telegraph.co.uk. 23 December 2018. Archived from the original on 16 August 2019. Retrieved 23 December 2018.
- Amos, Jonathan (29 December 2018). "Anak Krakatau: Indonesian volcano's dramatic collapse". BBC News. Archived from the original on 2 February 2022. Retrieved 4 May 2022.
- "Number of injured in Indonesia tsunami surges to over 14,000". The Star Online. Asean Plus. 31 December 2022. Archived from the original on 29 July 2019. Retrieved 31 December 2018.
- Associated Press (29 December 2022). "Volcano that triggered tsunami now a quarter of its pre-eruption size". NBC News. Archived from the original on 12 October 2019. Retrieved 4 May 2022.
- "22-23 Dec 2018 Eruption & Tsunami of Krakatoa - Updates". Volcano Discovery. 25 December 2018. Archived from the original on 9 June 2019. Retrieved 26 December 2018.
- Walter, Thomas R.; Haghshenas Haghighi, Mahmud; Schneider, Felix M.; Coppola, Diego; Motagh, Mahdi; Saul, Joachim; Babeyko, Andrey; Dahm, Torsten; Troll, Valentin R.; Tilmann, Frederik; Heimann, Sebastian (1 October 2019). "Complex hazard cascade culminating in the Anak Krakatau sector collapse". Nature Communications. 10 (1): 4339. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-12284-5. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 6773710. PMID 31575866.
- Amos, Jonathan (29 December 2018). "Indonesian volcano's lost stature". BBC News. Archived from the original on 2 February 2020. Retrieved 29 December 2018.
- Amos, Jonathan (10 January 2019). "Anak Krakatau: Finnish radar satellite eyes tsunami volcano". BBC News. Archived from the original on 26 May 2019. Retrieved 10 January 2019.
- "Krakatau volcano (Indonesia) activity update and field report: increasing unrest". www.volcanodiscovery.com. Volcano Discovery. 25 May 2019. Archived from the original on 25 May 2019. Retrieved 12 June 2019.
- Fiqih, Moch; Prawira, Adjie; Dipa, Arya (11 April 2020). "Anak Krakatau erupts, loud rumble heard in virus-stricken Greater Jakarta". The Jakarta Post. Archived from the original on 14 April 2020. Retrieved 6 January 2021.
- Dan Satherley (11 April 2020). "Eruption at Indonesian volcano Krakatoa". Newshub. Archived from the original on 11 April 2020. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- "Indonesia's Anak Krakatoa spews ash 1,500 metres high". South China Morning Post. 5 February 2022. Archived from the original on 5 February 2022. Retrieved 5 February 2022.
- Post, The Jakarta. "Anak Krakatau volcano erupts, spews huge ash tower". The Jakarta Post. Archived from the original on 27 April 2022. Retrieved 27 April 2022.
- Sennert, Sally Kuhn. "Global Volcanism Program | Report on Krakatau (Indonesia) — 20 April-26 April 2022". volcano.si.edu. Global Volcanism Program Smithsonian Institution. Archived from the original on 4 May 2022. Retrieved 4 May 2022.
- Peacock, Alice (27 April 2022). "'Child of Krakatoa' volcano triggers tsunami warning after continuous eruptions". mirror. Archived from the original on 27 April 2022. Retrieved 27 April 2022.
- "BMKG warns of possible tsunami as 'Child of Krakatoa' alert level raised | Coconuts". Coconuts Jakarta. 26 April 2022. Archived from the original on 27 April 2022. Retrieved 27 April 2022.
External links
 Media related to Anak Krakatoa at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Anak Krakatoa at Wikimedia Commons