2-Iodobenzoic acid
2-Iodobenzoic acid, or o-iodobenzoic acid, is an organic compound with the formula IC6H4COOH. The synthesis of 2-iodobenzoic acid via the diazotization of anthranilic acid is commonly performed in university organic chemistry labs. One of its most common uses is as a precursor for the preparation of IBX and Dess–Martin periodinane, both used as mild oxidants.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Iodobenzoic acid | |
| Other names
o-Iodobenzoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.682 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H5IO2 | |
| Molar mass | 248.018 |
| Density | 2.25 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 162 °C (324 °F; 435 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Synthesis
2-Iodobenzoic acid can be synthesized via a Sandmeyer reaction consisting of the diazotization of anthranilic acid followed by a diazo replacement. First anthranilic acid is treated with nitrous acid in order to convert the amino group into the diazo group. The diazo group is ejected, yielding a carbocation which is then attacked by highly nucleophilic I− anion.
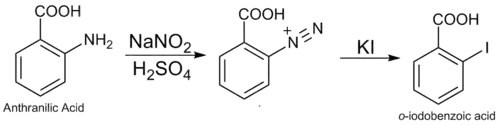
The nitrous acid is usually generated in situ from sodium nitrite.
References
Loda